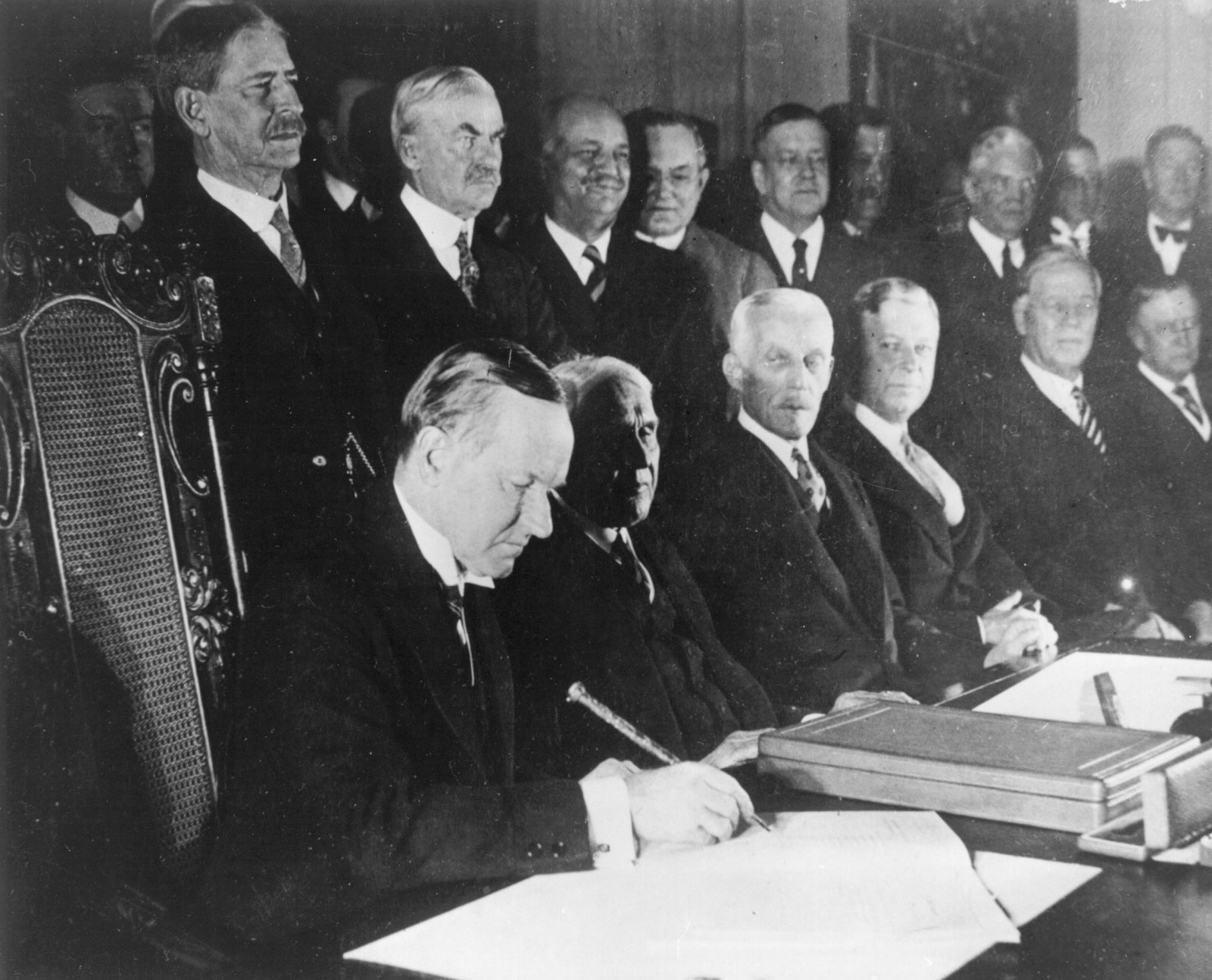
The Kellogg-Briand Pact of 1928 stands as a significant milestone in international relations, aiming to promote peace and prevent future wars. This treaty, initiated by U.S. Secretary of State Frank B. Kellogg and French Foreign Minister Aristide Briand, sought to outlaw war as a means of resolving conflicts. In a world still reeling from the devastation of World War I, the pact represented a hopeful yet ambitious attempt to establish a framework for global peace. In this article, we will delve into the origins, implications, and legacy of the Kellogg-Briand Pact, shedding light on its relevance in today’s world.
The Kellogg-Briand Pact was initially signed on August 27, 1928, by 15 nations, later expanding to 62 signatories. The treaty's core principle was simple: nations would renounce war as a means of solving disputes. However, the practicality and effectiveness of the pact were widely debated, leading to questions about its actual impact on international relations. Understanding the context in which the pact was formed and its subsequent historical journey is crucial for grasping its significance in modern diplomacy.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore various aspects of the Kellogg-Briand Pact, including its historical background, the key figures involved, the pact's provisions, and its long-term effects on international law and peace efforts. By examining these elements, we can better appreciate the challenges and aspirations of the global community in the quest for lasting peace.
Table of Contents
- Historical Background of the Kellogg-Briand Pact
- Key Figures Behind the Pact
- Provisions of the Pact
- Signatories and Their Roles
- Impact on International Law
- Challenges Faced by the Pact
- Legacy of the Kellogg-Briand Pact
- Conclusion
Historical Background of the Kellogg-Briand Pact
The roots of the Kellogg-Briand Pact can be traced back to the aftermath of World War I, a conflict that caused unprecedented destruction and loss of life. The Treaty of Versailles, which formally ended the war, aimed to establish a framework for peace but also sowed the seeds of future conflicts. Countries were grappling with the harsh realities of war, including economic instability and political upheaval.
In this climate of despair and disillusionment, the idea of a treaty to outlaw war gained traction. The rise of pacifist movements and public sentiment against military conflict created an environment ripe for diplomatic negotiations. The Kellogg-Briand Pact emerged as a response to these sentiments, reflecting a collective yearning for peace among nations.
Key Figures Behind the Pact
The Kellogg-Briand Pact was primarily the brainchild of two influential statesmen: Frank B. Kellogg and Aristide Briand. Their vision and diplomatic skills played a crucial role in shaping the treaty.
Frank B. Kellogg
Frank B. Kellogg served as the U.S. Secretary of State from 1925 to 1929. He was a prominent advocate for disarmament and international cooperation, believing that diplomatic efforts could prevent future conflicts. His commitment to peace was a driving force behind the initiation of the Kellogg-Briand Pact.
Aristide Briand
Aristide Briand was the French Foreign Minister and a key proponent of the pact. He envisioned a Europe united in peace and cooperation, seeking to mend the wounds left by World War I. His partnership with Kellogg was instrumental in bringing the pact to fruition.
Provisions of the Pact
The Kellogg-Briand Pact is relatively short and straightforward, consisting of only a few articles. Its main provisions include:
- Nations commit to renouncing war as an instrument of national policy.
- Disputes between nations should be resolved through peaceful means.
- The pact emphasizes the importance of diplomacy and negotiation in international relations.
Signatories and Their Roles
Initially, 15 nations signed the Kellogg-Briand Pact, including major powers like the United States, France, Germany, and the United Kingdom. Over time, the number of signatories grew to 62, reflecting widespread support for the treaty.
Key Signatories
- United States
- France
- United Kingdom
- Germany
- Japan
Impact on International Law
The Kellogg-Briand Pact had a profound impact on the development of international law, particularly in the realm of conflict resolution. It laid the groundwork for subsequent treaties and conventions aimed at promoting peace. Some key impacts include:
- It established a precedent for international agreements focused on peace.
- The pact influenced the creation of the United Nations and its charter, which emphasizes the importance of peaceful conflict resolution.
- It contributed to the formulation of the principles of collective security.
Challenges Faced by the Pact
Despite its noble intentions, the Kellogg-Briand Pact faced significant challenges and criticisms:
- Lack of enforcement mechanisms: The pact did not establish any means of enforcement, making it difficult to hold nations accountable.
- Failure to prevent wars: The pact could not prevent subsequent conflicts, including World War II, raising questions about its effectiveness.
- Ambiguity in definitions: The treaty lacked clear definitions of aggression and war, leading to varied interpretations.
Legacy of the Kellogg-Briand Pact
The legacy of the Kellogg-Briand Pact is multifaceted. While it did not achieve its primary goal of eliminating war, it played a crucial role in shaping international norms regarding conflict resolution. The pact is often viewed as a symbol of the idealism that characterized the interwar period.
Furthermore, the principles established by the pact continue to resonate in contemporary discussions about peace and security. The importance of diplomacy, dialogue, and peaceful coexistence remains central to international relations today.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Kellogg-Briand Pact of 1928 represents a significant attempt to outlaw war and promote peace among nations. Despite its limitations and the challenges it faced, the pact laid important groundwork for future efforts in international diplomacy and conflict resolution. As we reflect on the lessons of history, it is clear that the pursuit of peace is an ongoing journey that requires commitment, cooperation, and a willingness to engage in dialogue.
We invite you to share your thoughts on the relevance of the Kellogg-Briand Pact in today's world. Please leave a comment below, and consider sharing this article with others interested in the history of international relations.
We hope you found this exploration of the Kellogg-Briand Pact informative and engaging. We encourage you to return for more articles on significant historical events and their lasting impacts.
You Might Also Like
Los Angeles County Superior Court Docket Search: A Comprehensive GuideExploring The Luxurious World Of Vanity Baths: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlock Temporarily Locked Snapchat: A Comprehensive Guide
Pele Club Team: The Legacy Of A Football Icon
Discovering The Dragon Force Guitar: A Journey Through Speed And Melody
Article Recommendations
- Nfl Player Killed Yesterday
- Avatar Unalaq
- Bat House For Garden
- Skeet Ulrich Scream
- M Moggers Restaurant Pub
- Biomedical Science
- Megyn Kelly Before And After Weight Loss
- Projection Of A Onto B
- Pacifica Seafood El Paseo
- Blue Hanfu