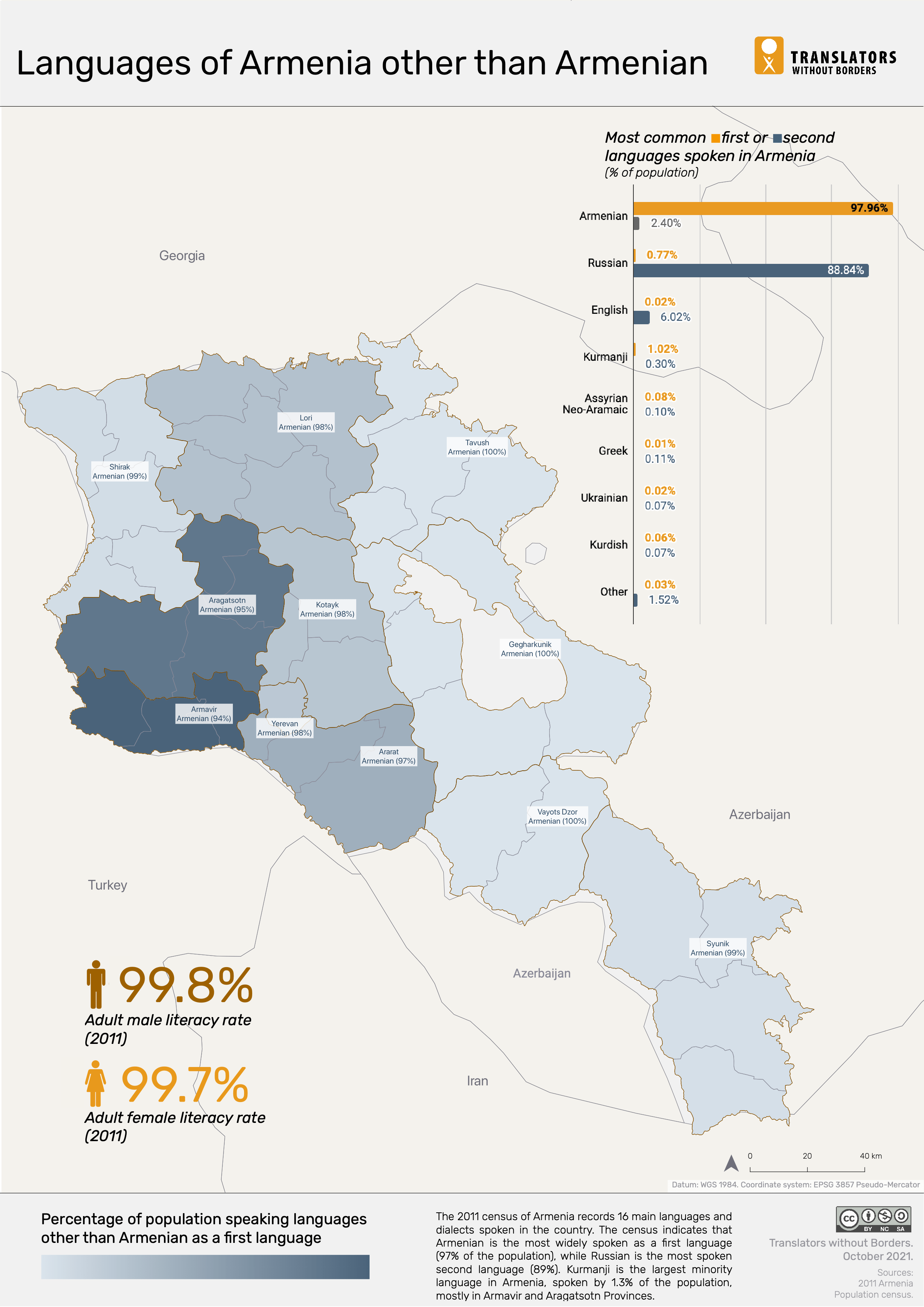
Armenia is a country rich in culture, history, and linguistic diversity. The official language of Armenia is Armenian, a unique and ancient language that has evolved over centuries. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the Armenian language, its historical significance, and the various dialects spoken in different regions of Armenia. We will also explore the relationship of Armenian with other languages and its importance in the global context.
Understanding the language spoken in Armenia is essential not only for those interested in visiting or studying the region but also for linguists and historians who seek to comprehend the evolution of languages. Armenian is not just a means of communication; it is a vital part of the Armenian identity and heritage, reflecting the nation’s resilience and cultural richness. This article aims to provide an in-depth look at the Armenian language and its significance.
As we navigate through this article, we will cover the origins of the Armenian language, its dialects, and its current status in contemporary society. Whether you are a traveler, a student of languages, or simply curious about Armenia, this comprehensive guide will equip you with valuable insights into what language does Armenia speak and the nuances that come with it.
Table of Contents
- 1. Overview of the Armenian Language
- 2. Historical Development of Armenian
- 3. Dialects of the Armenian Language
- 4. The Alphabet and Writing System
- 5. Armenian in the Modern World
- 6. The Influence of Other Languages
- 7. Learning Armenian: Resources and Tips
- 8. Conclusion
1. Overview of the Armenian Language
The Armenian language is an Indo-European language that stands out due to its unique characteristics and historical significance. It has its own alphabet, which was created by the scholar Mesrop Mashtots in the early 5th century. The language has approximately 6 million speakers worldwide, primarily in Armenia and the Armenian diaspora.
Armenian belongs to its own branch of the Indo-European language family, which distinguishes it from other languages in the region. The language is divided into two main dialects: Eastern Armenian and Western Armenian, each with its own phonetic and grammatical rules.
2. Historical Development of Armenian
The history of the Armenian language can be traced back to the 5th century, with the earliest written records appearing in the form of religious texts. Over the centuries, Armenian has undergone significant changes due to various historical events, including invasions, migrations, and cultural exchanges.
In the early Middle Ages, Armenian literature flourished, and the language became a medium for expressing the rich cultural and religious identity of the Armenian people. The translation of the Bible into Armenian in the 5th century was a monumental achievement that cemented the language's significance in Armenian culture.
2.1. Ancient Armenian
The ancient form of Armenian, known as Classical Armenian or Grabar, was used in religious and literary texts until the 19th century. Grabar is still studied and revered in Armenian culture today, serving as a connection to the country's historical roots.
2.2. Modern Armenian
Modern Armenian emerged in the 19th century, leading to significant linguistic reforms. Eastern Armenian is primarily spoken in Armenia, while Western Armenian is spoken by the Armenian diaspora, particularly in countries like Lebanon, France, and the United States.
3. Dialects of the Armenian Language
As previously mentioned, Armenian has two primary dialects: Eastern Armenian and Western Armenian. Each dialect has its own distinct characteristics, influencing pronunciation, vocabulary, and grammar.
3.1. Eastern Armenian
Eastern Armenian is the official language of the Republic of Armenia and is characterized by its use of the Yerevan dialect in the capital city. This dialect has been influenced by Russian and Persian due to historical ties.
3.2. Western Armenian
Western Armenian, on the other hand, has developed in the diaspora and retains many features from the language as it was spoken before the Armenian Genocide in the early 20th century. This dialect has been influenced by Turkish and French, reflecting the regions where Armenian communities are found.
4. The Alphabet and Writing System
The Armenian alphabet consists of 38 letters, designed by Mesrop Mashtots in 405 AD. The alphabet is unique and has a distinctive appearance, making it one of the oldest alphabets still in use today.
The Armenian script is essential for preserving the language and culture, allowing for the documentation of literary works, historical texts, and religious manuscripts.
5. Armenian in the Modern World
Today, Armenian is a thriving language spoken by millions. In Armenia, it serves as a crucial part of national identity and culture. The government promotes the use of Armenian in education, media, and public life, ensuring its continued relevance.
With the rise of technology and the internet, there are many resources available for those interested in learning Armenian, including online courses, language apps, and social media groups.
6. The Influence of Other Languages
Due to its geographical location, Armenian has been influenced by several languages over time, including Greek, Persian, Arabic, Turkish, and Russian. These influences can be seen in the vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, and pronunciation of Armenian.
Understanding these influences can provide insight into the rich tapestry of Armenian culture and history, showcasing the resilience and adaptability of the language.
7. Learning Armenian: Resources and Tips
For those interested in learning Armenian, there are several effective resources available:
- Language Apps: Apps like Duolingo and Drops offer Armenian language courses.
- Online Courses: Websites such as Armenian Language Institute provide structured lessons.
- Books: There are various textbooks and workbooks available for self-study.
- Community Groups: Joining Armenian community groups can provide practice opportunities and cultural immersion.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, the Armenian language is a vital part of the nation's identity, embodying centuries of history and culture. Understanding what language Armenia speaks not only enriches our knowledge of the region but also highlights the importance of preserving linguistic diversity in our global society. We encourage you to explore more about this fascinating language, perhaps even considering learning it yourself!
What are your thoughts on the Armenian language? Have you ever considered learning it? Please leave your comments below, share this article with others, and feel free to explore more articles on our site!
Thank you for reading, and we hope to see you again soon!
You Might Also Like
The Enigmatic World Of The Doctor's Companion: A Comprehensive Guide To The Peri Brown From Doctor WhoThe Legend Of Zelda: The Master Sword - A Comprehensive Exploration
Understanding 6 Speed Dual Clutch: Meaning, Benefits, And More
Best Law Firm In New York: Your Ultimate Guide To Legal Excellence
Comprehensive List Of Malayalam Cinema: A Deep Dive Into The Heart Of Indian Film
Article Recommendations
- Dave Coulier
- Ubuntu Install Deb File Command Line
- Echinacea For Sore Throat
- Are Egg Cartons Recyclable
- Projection Of A Onto B
- Cecelia Name
- Harvard Rejection
- Saxon Musk
- Joe Metheny
- Kelly Roland Cannes